Given how technology is constantly advancing in developed countries, it’s surprising to learn that the average life expectancy is decreasing in the United States. Countless new discoveries are made nearly every day in regards to how we can improve our health and overall quality of life — yet, Americans are continuing to die way before their time.
Researchers have several theories as to why life expectancy has been shortened in the US. For instance, the obesity epidemic — which affects more than one-third of Americans — increases the risk for type two diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. All of these conditions can lead to an early death. Environmental pollution and opioid addiction are also cited as major causes behind shortened US life expectancy.
In 2015, the life expectancy of Americans dropped for the first time since 1993. There were 86,212 more deaths in 2015 than there were in 2014. The CDC reports that opioids killed more than 33,000 people in 2015, which was more deaths caused by opioids than any other year on record.
Opioids are highly addictive, and are causing an uptick in overdoses around the country. The majority of overdose deaths are unintentional, and occur when people misuse their prescriptions, or are suffering from addiction. Opioid addiction is a serious, chronic relapsing brain condition that can be effectively treated both physically and psychologically with proper intervention.
As long as the opioid epidemic continues to plague America, our country’s life expectancy will continue to decrease, and go on to affect future generations — including our own children and grandchildren.
Here’s a closer look at how the opioid epidemic is affecting the quality of life of Americans, and at what is being done to end this serious national crisis.
What Are Opioids, and What Is the Opioid Epidemic?
Opioids, also known as painkillers, are commonly prescribed to treat moderate to severe pain such as that caused by injury, surgery, and cancer treatments. Heroin, which is an illicit opioid, is considered the most highly addictive drug in the world. Other common painkillers include fentanyl, oxycodone, and morphine.
Since opioids are highly addictive, these drugs are generally prescribed on a short-term basis to lower the risk for physical dependence and addiction. But when people misuse their medications or take opioids for an extended period of time, they face a higher risk for overdose and death. Opioid addiction is now a nationwide crisis contributing to thousands of unintentional deaths across the US every year.
The opioid crisis has recently been declared a national emergency by the White House. Governors are taking steps on the state level to decrease opioid addiction and overdose deaths, such as updating prescription monitoring databases to reduce doctor shopping, and expanding access to opioid addiction treatments. Many US doctors are continuing to overprescribe opioids, which has urged the CDC into issuing new prescribing guidelines surrounding the use of opioids for treating chronic pain.
Certain opioids are more dangerous and deadly than others due to their potency levels and the way these drugs are manufactured. Many illicit opioids sold on the street are synthetic, and manufactured overseas in China using a cocktail of dangerous chemicals and ingredients. Using opioids just one time can trigger an overdose and lead to coma or death.
Dangerous Opioids List
- Carfentanil. This illicit elephant tranquilizer is up to 10,000 times more potent than morphine, and is frequently mixed or cut with heroin. Carfentanil can be purchased from the streets or online from the Deep web.
- Fentanyl. This potent painkiller is up to 100 times stronger than morphine. Synthetic fentanyl can be purchased from the Deep web or on the streets, and is often mixed or cut with heroin. In 2016, fentanyl caused more than 20,000 overdose deaths in the US.
- U-47700. Also known as Pink, this opioid is said to be nearly eight times stronger than morphine. This illicit opioid is sold on the streets, and can also be purchased online from the Deep web.
- Heroin. As the most highly addictive drug in the world, heroin caused nearly 13,000 overdose deaths in the US in 2015.
- Methadone. This drug is commonly used in opioid addiction treatment to curb opioid withdrawal symptoms, but can be addictive when misused.
- Oxycodone. This prescription opioid is also known as OxyContin or Oxy, and is the number one opioid prescribed in the US.
- Hydrocodone. This prescription opioid is commonly sold under the brand names Vicodin, Lorcet, and Norco.
- Morphine. This drug, which is also available under brand name Roxanol, is commonly used to relieve moderate to severe pain associated with surgery.
If you or someone you love is using any substances on the dangerous opioids list, talk to your doctor about alternative treatments that carry a lower risk for addiction, or familiarize yourself with common signs of opioid addiction. Many drug and alcohol rehab centers can help you safely and comfortably overcome opioid addiction with a lowered risk for health complications.
An Overview of US Life Expectancy Rates
The average life expectancy for Americans is 78.8 years, based on CDC data from 2015. Males have an average life expectancy of 76.3 years, while females live an average of 81.2 years. Overall life expectancy in the US decreased by 0.1 years from 2014 to 2015.
While 0.1 years may seem like a small decrease in terms of life expectancy, any decline at all is usually considered rare in developed countries like the US. The last time US life expectancy decreased substantially was in 1993, when this number dropped to 75.42 years. In 1993, low life expectancy was being driven by the AIDS epidemic, and factors including influenza, homicide, and accidental deaths.
Presently, the number one leading cause of death in the US is heart disease, followed by cancer, respiratory disease, and unintentional injuries, which comes in at number four. The majority of opioid overdoses are considered unintentional injuries, but opioid use disorder itself also increases the risk for heart disease — further indicating that opioid misuse and addiction may also be contributing to the nation’s leading cause of death.
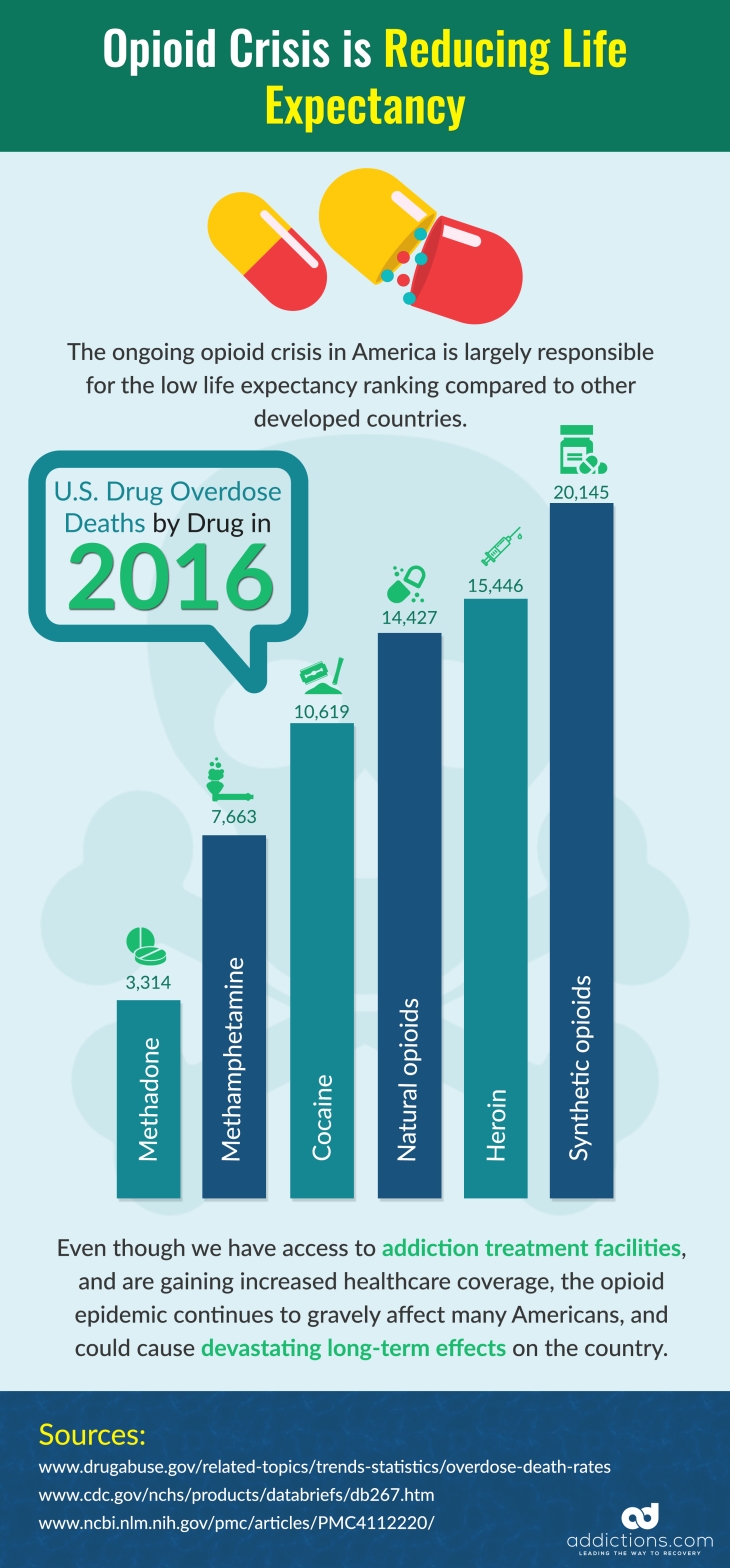
A new study conducted on the impact of opioid overdoses on US life expectancy found that opioids are taking 2.5 years away from the lives of Americans. The CDC is projecting that when 2016 numbers are finalized, opioid deaths may have contributed to over 64,000 deaths — more than the number of deaths of US soldiers who fought in the Vietnam War. Fentanyl, which is one of the most potent, deadly opioids, is now the leading causes of opioid overdoses, and is projected to cause more than double the deaths in 2017 than in 2016 with an expected death toll of 20,145.
How the US Compares to Other Countries
Compared to people who live in other developed, high-income nations, Americans tend to live far shorter lives. Research indicates that Americans tend to suffer from higher rates of disease and injury, and demonstrate a higher number of unhealthy lifestyle behaviors than men and women in other nations. Plus, an estimated 6.2 percent of the US population is addicted to prescription drugs — the majority of which are opioids.
The US is ranked 10th on the Human Development Index. The HDI uses education, income, and life expectancy rates to measure human development around the world. Countries ranking high in HDI generally have higher lifespans, higher education levels, and higher income per capita.
Top 10 countries on the HDI:
- Norway
- Australia
- Switzerland
- Germany
- Denmark
- Singapore
- Netherlands
- Ireland
- Iceland
- Canada and US
Here’s how those same countries rank in terms of life expectancy, as of 2016.
- Norway: Ranked 21st (81.80 years)
- Australia: Ranked 15th (82.20 years)
- Switzerland: Ranked 9th (82.60 years)
- Germany: Ranked 34th (80.70 years)
- Denmark: Ranked 47th (79.40 years)
- Singapore: Ranked 2nd (85.00 years)
- Netherlands: Ranked 25th (81.30 years)
- Ireland: Ranked 32nd (80.80 years)
- Iceland: Ranked 6th (83.00 years)
- Canada: Ranked 19th (81.90 years)
- USA: Ranked 42nd (79.80 years)
The US ranks 42nd for life expectancy out of all countries in the world. Monaco has the highest life expectancy of 89.5 years, followed by Singapore and Japan, which are tied at 85 years.
Neighboring country Canada ranks 19th with life expectancy at 81.9 years. While Canada and the US are tied for HDI, Canada’s life expectancy is much higher than that in the US. Canadian residents tend to use fewer prescription drugs, and are not currently facing a nationwide opioid epidemic like the US.
States With the Lowest Life Expectancy Rates
In the US, life expectancy varies from state to state by as much as six years. Hawaii has the highest life expectancy of 81.3 years, and the second lowest obesity rate. However, more than 36 percent of Hawaii residents are of Asian ethnicity and come from Asian cultural backgrounds — indicating that the lifestyle practices of these residents may be generally healthier than their American counterparts.
Mississippi has the lowest life expectancy rate of 75 years, and the third-highest obesity rate. Mississippi also has some of the highest poverty and unemployment rates, and education levels that fall far below the national average.
Top 10 states with the lowest life expectancy:
- Mississippi: 75.0 years
- West Virginia: 75.4 years
- Alabama: 75.4 years
- Louisiana: 75.7 years
- Oklahoma: 75.9 years
- Arkansas: 76.0 years
- Kentucky: 76.0 years
- Tennessee: 76.3 years
- District of Columbia: 76.5 years
- South Carolina: 77.0 years
Washington, DC is ranked number one out of the 10 most drug-addicted states in America and struggles mostly with painkiller addiction and overdoses. Alcohol, marijuana, and cocaine are also widely misused throughout DC, and lend to the state’s low life expectancy rate.
When looking at life expectancy by county, the variances are even more alarming than that between states in certain areas of the US. For instance, Oglala Lakota County in South Dakota has the lowest life expectancy at 67 years, while Summit, Pitkin, and Eagle counties in Colorado all have high life expectancy rates of over 85 years. Experts say life expectancy may be lower in certain counties on behalf of factors such as lower income and high obesity rates, but there is no hard data that reveals exact causes of low life expectancy by county.
The Importance of Opioid Addiction Treatment in the U.S.
Many counties across the US lack access to effective medical treatments for opioid addiction. For instance, many rural areas lack treatment centers, making it difficult for local residents to be connected with opioid addiction treatment. Factors such as weather and low income are also barriers to opioid addiction treatment in certain parts of some states.
Among the most effective opioid addiction treatments available in the US are medication-assisted treatments involving the use of buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone. These drugs have the ability to reduce heroin and painkiller withdrawal symptoms so patients can recover more safely and comfortably, and benefit from a lower risk for relapse following treatment. Many times, these medications are combined with therapies that help patients overcome psychological causes behind their opioid addiction.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy helps patients identify and overcome negative thoughts and behaviors driving their addiction. Ongoing twelve-step support groups like Narcotics Anonymous help patients stay clean for life, while group and family counseling help patients repair and rebuild relationships that may have suffered on behalf of opioid addiction.
Opioid addiction treatment allows patients to improve their health and overall quality of life by helping them find ways to cope with life’s stressors without relying on drugs. Raising awareness about opioid addiction treatment, and increasing access to these treatments can greatly help reduce US overdose rates, and the number of unintentional deaths caused by opioid overdoses.